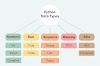
Literals
Literal in Python: A literal in Python is a notation used to represent a fixed value in the source code. It is a direct way of expressing values such as numbers, strings, and booleans. Literals are used to assign constant values to variables or directly use them in expressions.
 |
Numeric Literals:
Integer literals: Whole numbers without a fractional component.
integer_literal = 42
String Literals:
Single-quoted or double-quoted strings.
single_quoted_literal = 'Hello, World!'
double_quoted_literal = "Python is awesome!"- Triple-quoted strings for multiline strings.
- multiline_literal = """This is a multiline string."""
Boolean Literals:
TrueandFalseare the boolean literals in Python.- boolean_literal_true = True boolean_literal_false = False
None Literal:
Nonerepresents the absence of a value or a null value.- none_literal = None
List Literals:
- Lists are created using square brackets
[]. - list_literal = [1, 2, 3, 4]
Tuple Literals:
- Tuples are created using parentheses
(). - tuple_literal = (1, 'two', 3.0)
Set Literals:
- Sets are created using curly braces
{}. - set_literal = {1, 2, 3, 3} # Note: Sets do not allow duplicate elements
Dictionary Literals:
- Dictionaries are created using curly braces
{}with key-value pairs. - dict_literal = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
Uses of literals
Difference blw Literal and Constants
Literal:
A literal is the actual value assigned to a variable or used directly in an expression. It is a representation of a fixed value in the source code.
Constant:
In Python, constants are more of a convention rather than a language-enforced concept. Constants are variables whose values are not intended to be changed during the execution of a program. Typically, constants are represented by uppercase variable names to indicate that their values should not be modified.
Summary
Numeric Literals:
Q: What is a numeric literal in Python?
- A: A numeric literal represents a specific value of a numeric type, such as integers or floating-point numbers.
Q: Can you provide examples of integer literals in Python?
- A: Examples of integer literals are
42,-10, and0.
- A: Examples of integer literals are
Q: How are floating-point literals represented in Python?
- A: Floating-point literals include decimal points or use scientific notation, such as
3.14or2.5e-3.
- A: Floating-point literals include decimal points or use scientific notation, such as
String Literals:
Q: What is a string literal, and how is it defined in Python?
- A: A string literal represents a sequence of characters and is defined using single (
') or double (") quotes.
- A: A string literal represents a sequence of characters and is defined using single (
Q: Can you provide examples of string literals in Python?
- A: Examples of string literals are
'Hello',"Python", and'''Multi-line string'''.
- A: Examples of string literals are
Q: How do you include special characters in a string literal?
- A: Special characters in a string can be represented using escape sequences, like
"\n"for a newline.
- A: Special characters in a string can be represented using escape sequences, like
Boolean and None Literals:
Q: What are Boolean literals in Python?
- A: Boolean literals represent the truth values
TrueorFalse.
- A: Boolean literals represent the truth values
Q: How is the None literal used in Python?
- A: The
Noneliteral represents the absence of a value or a null value.
- A: The
List and Tuple Literals:
Q: What is a list literal in Python?
- A: A list literal represents a sequence of values enclosed in square brackets, such as
[1, 2, 3].
- A: A list literal represents a sequence of values enclosed in square brackets, such as
Q: Can you define a tuple literal in Python?
- A: A tuple literal represents an ordered, immutable sequence of values and is defined using parentheses, like
(1, 2, 3).
- A: A tuple literal represents an ordered, immutable sequence of values and is defined using parentheses, like
Set and Dictionary Literals:
Q: How is a set literal represented in Python?
- A: A set literal represents an unordered collection of unique values and is defined using curly braces, such as
{1, 2, 3}.
- A: A set literal represents an unordered collection of unique values and is defined using curly braces, such as
Q: What does a dictionary literal look like in Python?
- A: A dictionary literal represents a collection of key-value pairs enclosed in curly braces, like
{'key': 'value', 'age': 25}.
- A: A dictionary literal represents a collection of key-value pairs enclosed in curly braces, like
Boolean Operations:
Q: What is the result of the
andoperation betweenTrueandFalse?- A: The result is
Falsebecauseandrequires both operands to beTrue.
- A: The result is
Q: How does the
oroperation behave withTrueandFalseoperands?- A: The result is
Trueif at least one operand isTrue.
- A: The result is
String Operations:
Q: How do you concatenate two strings in Python?
- A: Strings can be concatenated using the
+operator, like"Hello" + " " + "World".
- A: Strings can be concatenated using the
Q: What does the
*operator do with a string literal?- A: The
*operator repeats a string a specified number of times. For example,"Python" * 3results in"PythonPythonPython".
- A: The
Numeric Operations:
- Q: How is exponentiation represented in Python?
- A: Exponentiation is represented using the
**operator. For example,2 ** 3is 8.
- A: Exponentiation is represented using the
Byte and Bytearray Literals:
Q: What is a byte literal in Python?
- A: A byte literal represents a sequence of bytes and is defined using the
bprefix, likeb'hello'.
- A: A byte literal represents a sequence of bytes and is defined using the
Q: How does a bytearray literal differ from a byte literal?
- A: A bytearray literal is mutable, allowing modifications, while a byte literal is immutable.
Complex Number Literals:
- Q: How are complex number literals represented in Python?
- A: Complex number literals include a real part and an imaginary part, such as
3 + 4j.
- A: Complex number literals include a real part and an imaginary part, such as




0 Comments